Using Norton theorem, find the equivalent Norton circuit for the highlighted circuit aross terminals a-b.
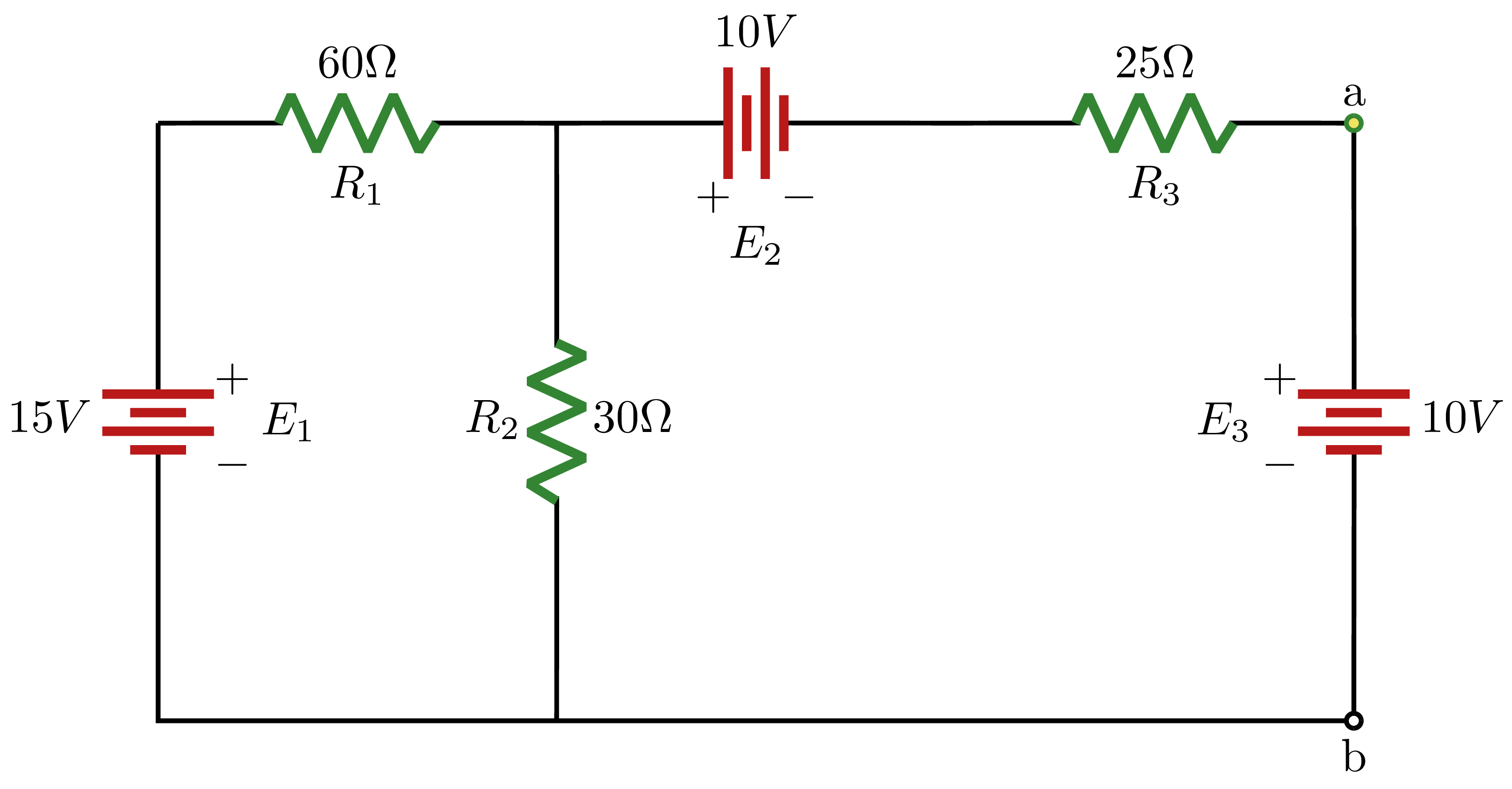
Solving for $R_{N}$
$$\begin{align}
R_{N} &= (R_1 //R_2) + R_3\\
&= \frac{(60\Omega) \cdot (30 \Omega)}{(60\Omega) + (30 \Omega)} + 25\Omega \\
&= 20\Omega + 25\Omega \\
&=45\Omega
\end{align}
$$
Using superposition to solve for $I_N$
$I'_N$: $E_1$ ON $E_2$ OFF
$$\begin{align}
\text{Solve for the voltage across $R_2$//$R_3$:} \rightarrow R_{23} &= \frac{R_2 \cdot R_3}{R_2 + R_3}\\
&= \frac{(30\Omega) \cdot (25\Omega)}{30\Omega + 25\Omega}\\
&= 13.64\Omega\\
\rightarrow V_{23} &= \frac{R_{23}}{R_1+R_{23}}\cdot E_1\\
&=\frac{13.64\Omega}{(60+13.64)\Omega}\cdot 15V\\
&=\frac{13.64}{73.64}\Omega\cdot 15V\\
&=2.778V\\
\therefore I'_N &= \frac{V_{23}}{R_3}\\
&=\frac{2.778V}{25\Omega}\\
&=111.1 mA
\end{align}
$$
$I''_N$: $E_1$ OFF $E_2$ ON
$$\begin{align}
\text{Solve for the total resistance:} \rightarrow R_{T} &= R_1 // R_2 + R_3\\
&=\frac{R_1 \cdot R_2}{R_1 + R_2}+R_3\\
&= \frac{(60\Omega) \cdot (30\Omega)}{60\Omega + 30\Omega}+25\Omega\\
&= 20\Omega+ 25\Omega\\
&=45\Omega\\
\therefore I''_N &= \frac{-E_{2}}{R_T}\\
&=\frac{-10V}{45\Omega}\\
&=-222.2 mA
\end{align}
$$
Solving for $I_N$
$$\begin{align}
I_N &= I'_N - I''_N\\
&=111.1mA - 222.2mA\\
&=-111.1 mA
\end{align}
$$