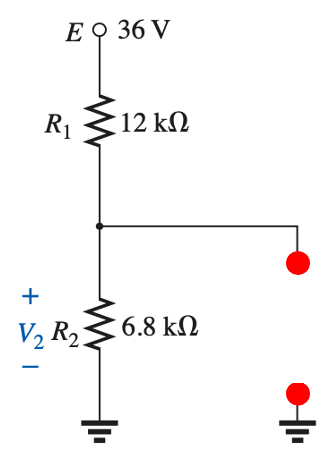
Using superposition, find the voltage $V_2$ across the $6.8k\Omega$ resistor for the network of the figue below.
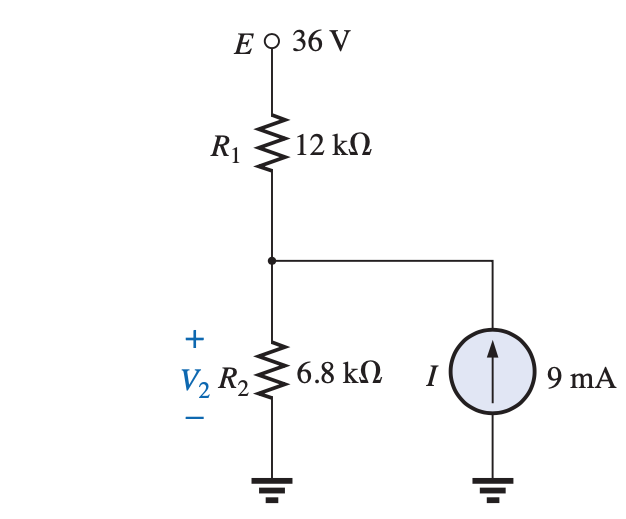
which is the same as
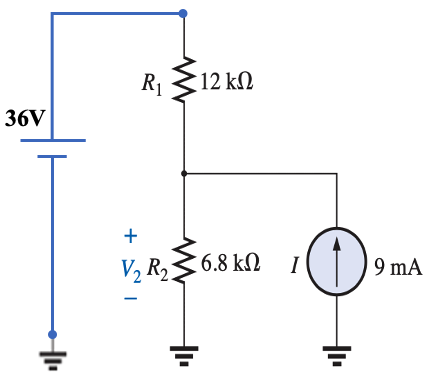
Simulation:
Using simulation as a guide, the circuit parameters will be as in the figue below.
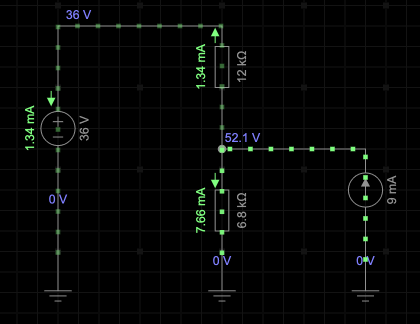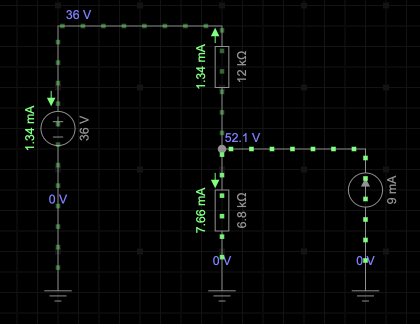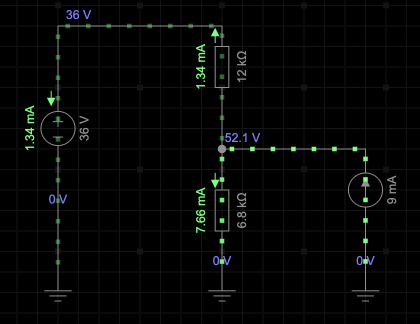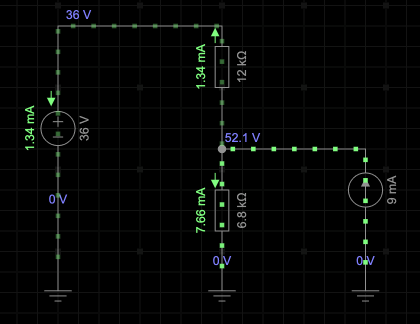
Solution:
First we turn the battery off and solve for the voltage $V'_2$ across $R_2$. Then we turn off the current source $I$ and solve for the $V''_2$ due to the 36V battery.
Step 1: I (ON) E (OFF)
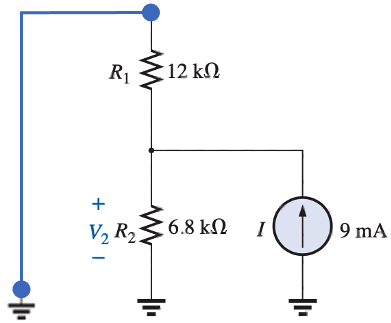
We can use the current divider rule to find the current through $R_2$ then use Ohm's law to find the voltage $V_2$:
$$\begin{align}\text{Current divider rule: }\rightarrow I'_{2} &= \frac{R_1}{(R_1+R_2)}\cdot I \\
&=\frac{12 k\Omega}{(12 k\Omega + 6.8k\Omega)}\cdot 9mA \\
&=\frac{12 k\Omega}{18.8 k\Omega }\cdot 9mA \\
&=0.638\cdot 9mA \\
&=5.745mA\\
\text{Ohm's law: }\rightarrow V'_2 &= R_2 \cdot I'_{2}\\
&=6.8k\Omega \cdot 5.75mA\\
&=(6.8\times 10^3) \cdot (5.75\times 10^{-3})\\
&= 39.06 V\end{align}$$
Step 2: I (OFF) E (ON)
which is equivalent to
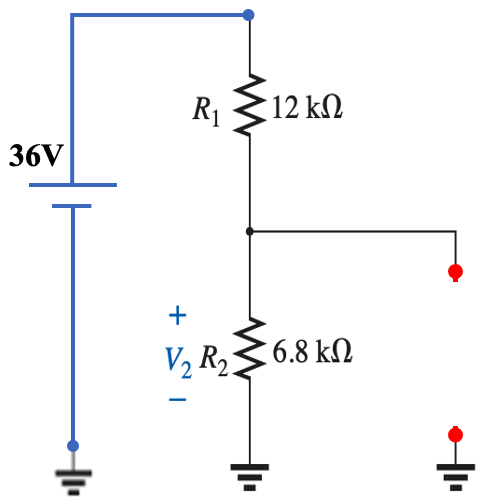
Since $R_3$ is in parallel with the battery, then the voltage across it is the battery voltage and it wont affect the current through $R_1$.
To solver for the current through $R_1$, we will only consider the resistances on the left side of the battery
$$\begin{align}\text{Voltage divider rule: }\rightarrow V''_{2} &= \frac{R_2}{(R_1+R_2)}\cdot E\\
&=\frac{6.8 k\Omega}{(12 k\Omega + 6.8 k\Omega)} \cdot 36 V\\
&=\frac{6.8 k\Omega}{18.8 k\Omega } \cdot 36 V\\
&= 13.02 V \end{align}$$
Step 3: Solving for $V_2$
$$\begin{align*} V_2 &= V'_2 + V''_2 \\
&= 39.06 V + 13.02 V\\
&= 52.08 V \end{align*}$$